Key Takeaways
Telematics is the technology used to monitor a wide range of information relating to an individual vehicle or an entire fleet. Telematics systems gather data including vehicle location, driver behavior, engine diagnostics and vehicle activity, and visualize this data on software platforms that help fleet operators manage their resources.
Table of contents
- How does telematics work?
- Telematics and GPS Fleet Tracking
- Telematics past, present and future
- Telematics devices and software
- What telematics can do for your business
- The difference between GPS tracking and telematics
- Which vehicles can telematics be used for?
How does telematics work?
Fleet telematics gathers a range of data using Global Positioning System (GPS) technology, sensors and vehicle engine data to provide fleet operators with the information they need to manage their fleet.
- Global Positioning System (GPS) technology powers live visibility into vehicle location, speed and movement within points of interest through geofencing.
- Cameras and sensors enable the capture of data on driver activity, including aggressive acceleration, harsh braking and erratic cornering, but sensors can be used to monitor any in-vehicle activity such as a door opening, tail lift raising and even trailer temperature.
- Engine diagnostics solutions pull data directly from the in vehicle diagnostics system and are primarily used to gather real time data on fuel efficiency and vehicle odometer readings that help power digital fleet maintenance solutions.
- Driver apps are used to streamline processes and enable accurate operational data to be captured instantly. The most common applications are job management, pre-trip checklists, fatigue management and route compliance.
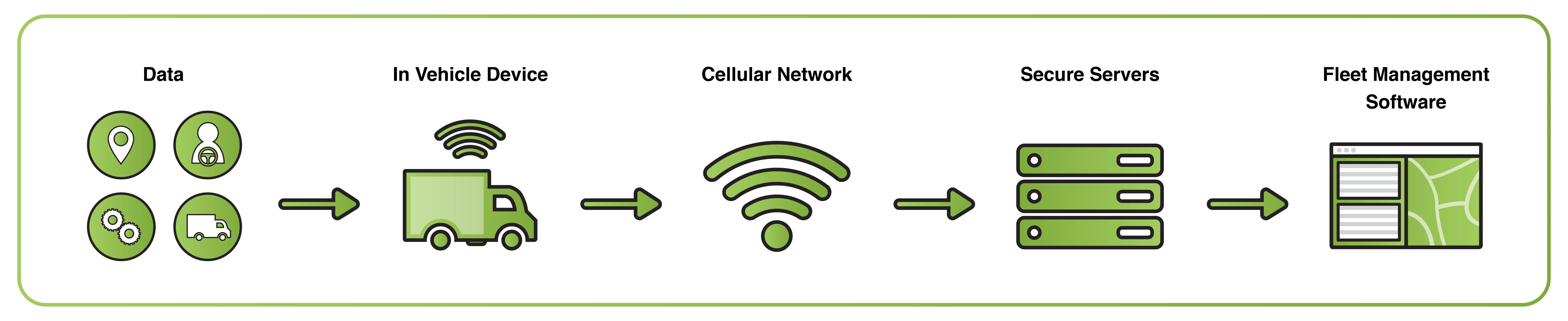
The data is temporarily stored in a telematics device that in installed in each vehicle, and is then transmitted over private cellular networks to secure servers. It is this central data hub that enables fleet management software to provide easy-to-understand visualisations that help fleet managers optimize their operation.
Telematics systems: past, present and future
Telematics technology developed out of the rapid expansion of the internet from the mid-1990s onwards. The greater availability and practicality of telecommunications technologies that arose in tandem with this expansion also produced new forms of remote communication. Over the years, these developed into what we now recognize as modern telematics systems, and these have been particularly widely adopted over the last decade.
Telematics systems now enable firms to manage fleets of all sizes – from a handful of vehicles to hundreds – and help businesses to improve safety, implement sustainable processes and streamline tasks. Telematics has now developed to the point where it goes well beyond asset tracking to incorporate vehicle and driver performance, workflow applications as well as maintenance management.
Telematics is also proving crucial in what has become known as the Internet of Things that Move (IoTtM); specifically, in transport and freight. These sectors have been leading adopters of IoT technology, with the data it provides allowing for more efficient routing and scheduling as well as resource optimization. The IoTtM encompasses, location tracking, driver monitoring, engine diagnostics and digital workflow.
The benefits of telematics:
Telematics systems provide fleet operations insight that enables them to improve resource utilisation, driver performance and productivity. Here are the 5 key benefits of the latest technology.
- Reduced fuel costs. With fuel consumption being one of the most pressing costs facing fleets, detecting and reducing excessive fuel use is absolutely crucial to overall efficiency. Telematics does this through more direct route planning, reducing job site bottlenecks and cutting engine idling, while also detecting unauthorized vehicle or equipment use (enabling firms to cut down on resulting fuel usage).
- More cost-effective maintenance. Telematics warns managers of mechanical issues with vehicles and equipment, which allows them to address these problems sooner and thereby reduce the danger of downtime (which is not only inconvenient but can also have serious knock-on effects for other jobs). It also makes scheduling preventative maintenance simpler, which again helps to maximize vehicle and equipment uptime.
- Better communication. Previously, keeping in touch with drivers and operators out in the field could be a complex business. Telematics simplifies communication processes and significantly reduces the need for human operators and drivers to check in and report back, automating much of this process. As well as ensuring that managers have access to the data they need faster, this allows operators to spend more time concentrating directly on the job in hand.
- Enhanced safety. Another crucial consideration (and a central legal responsibility) for firms operating fleets of vehicles and equipment, safety is of paramount importance. Telematics improves safety management by monitoring both driver and operative behavior, and vehicle and equipment performance. It allows anomalies – such as unsafe practices – to be detected and addressed quicker. It also allows for emergency assistance to be directed straight to the site where it is needed, through location tracking.
- Streamlined workflow. Businesses are always looking to find ways to build competitive advantage and connected driver apps enable them easily implement digital processes that reduce the administrative burden on drivers, enable instant data transfer and respond quickly to customer needs. With effective digital systems businesses can serve there customers better and increase profitability.
Telematics is also helping both industry and society adapt to the continuing challenges facing major towns and cities. The mounting pressure on urban infrastructure (particularly transport) requires industry to take innovative and imaginative measures; this has led to the rise of the so-called ‘smart city’. This means, in a nutshell, using data and technology to maximise efficiencies (from energy efficiency to traffic management) and thereby make urban environments more practical, sustainable, secure and liveable for all concerned.
Telematics devices and software
Most commonly, telematics data is collected by a small device installed in the vehicle (or other asset) itself. This collects stores and transmits different types of information relating to the vehicle’s performance, condition and usage. There are different types of telematics devices available that offer different functionality and benefits. The most accurate and secure telematics devices are hardwired, these devices offer tamper proof functionality and a wider range of connectivity to peripheral devices.
Telematics devices are often connected to other in-cab driver interfaces that enable drivers to receive jobs, capture proof of delivery, complete pre-trip inspections and even get real time feedback on their driving performance.
Choose the Right Telematics Device for Your Business
Teletrac Navman have developed an infrastructure that keeps you connected to almost any mobile asset. See how our range of telematics devices can be used across your business.
RE400 Rugged Device
This ruggedized IP68 rated device that captures detailed engine diagnostics data and location. Perfect for managing hard working heavy equipment.
ST101 Solar Powered Device
This solar-powered GPS tracker tracks all of your assets, construction equipment to trailers, containers and rental equipment in a single solution.
SI201 Self-Install Device
This self-install device that captures location, driver behavior, and engine diagnostics data. The device of choice when flexibility is key.
AT301 Battery Powered Device
Transferable battery-powered GPS device that can be easily attached to equipment. Perfect to track location, equipment movement, and maintenance.
VT101 Hardwired Device
Small hardwired device that captures location, engine diagnostics, and driver behaviour data. The perfect device for safety and compliance solutions.
What can telematics do for your fleet?
There are a number of ways that telematics systems benefit fleets across a wide range of industries, helping them to meet compliance requirements, improve driver safety and streamline processes. The primary industries that use telematics are:
- Freight and Transportation. Getting goods from one place to another is logistical challenge that requires planning and close monitoring to keep everything running smoothly. Telematics solutions help transport operations meet driver hours requirements with real-time tachograph data, improve job management with digital run sheets and enhance driver safety through performance monitoring and reward programs.
- Construction. Managing projects across multiple jobsites requires careful planning and detailed insight, so site managers can respond to issues quickly. Equipment telematics provides real time visibility into the location and utilisation of equipment helping to ensure that resources are effectively distributed, keeping jobs on track and rental costs to a minimum. With digital maintenance and inspection applications, construction operations can easily stay on top of preventative maintenance reducing unscheduled downtime whilst keeping operators safe.
- Retail and Manufacturing. Moving product efficiently, on-time and within the driver hours requires real-time visibility. Telematics platforms are used in retail and manufacturing to support route planning, implement efficient driving practices and streamline workflows, that help to reduce cost per mile and simplify the administrative burden on drivers.
- Hire and Rental. With high value assets being operated by different customers, planners want to have visibility into their usage, maintenance and location. Telematics systems provide equipment rental companies with the visibility to ensure that equipment is being operated correctly, that rental agreements aren't being violated and ensure that the equipment is being used in the specified location.
- Passenger Transport. The safety and satisfaction of customers is crucial to remain competitive in a congested market, with customers expecting vehicles to arrive on time and for safe driving practices to be followed. Telematics systems are used in passenger transport operations to improve routing, respond to traffic conditions, ensure that vehicles have been fully maintained and implement on-going driver training to improve safety.
Empower Your Business with Telematics
Gain real-time insights into your fleet's performance, improve efficiency, and optimise operations with Teletrac Navman's telematics solutions.
Telematics & Data Security
Data security is an important consideration when assessing telematics solutions. Telematics devices capture, store and transmit a huge amount of data across a range of different areas including location tracking, driver performance and vehicle condition and it is of the utmost importance that this data remains firmly safe and secure. Telematics providers take data protection seriously and implement a wide range of processes that cover physical security and cloud security.
Their is a large range of data points that are captured by telematics systems including the following:
- Vehicle location
- Geographical point of interest (Geofencing)
- Vehicle speed
- Vehicle incidents (harsh braking, acceleration and cornering)
- Vehicle diagnostics (e.g. EPM, MPG, odometer)
- Vehicle status (customizable)
- Remote vehicle inspection reports
- Panic alerts
- Job dispatch and messaging
- Electrical or sensor activity (via PTO)
- Dashboard camera footage
Which vehicles can telematics be used for?
Telematics is a versatile technology, both in the number of functions it can perform and the range of different vehicles and other assets with which it can be used. It is suitable for use with the following vehicles and assets, among others:
- Cars: As well as performing important productivity and vehicle maintenance functions for company car and sales fleets, telematics is also used to monitor private mileage and ensure health and safety compliance, an essential part of employers’ duty of care.
- Cargo vans/pickup trucks: Used for functions including job dispatch and routing, time on site reporting, time sheet reporting, proof of delivery solutions, monitoring unauthorized vehicle use and tracking driver behavior.
- Single axle/tractor units: Here, telematics helps with route optimization and scheduling, driver hour management, fuel management and driver behavior reporting.
- Buses and coaches: Telematics provides assistance with driver hour management, route optimization and scheduling, fuel management (including engine idling), integration of services (through, for example, time of arrival notifications) and driver behavior reporting.
- Heavy equipment: In the construction industry, telematics is used for heavy earth-moving equipment. Here it serves to boost jobsite productivity by tracking equipment utilisation, enabling preventative maintenance and reducing fuel burn.
- Specialist vehicles: Telematics is also widely used for a range of specialist vehicles, including dump trucks, tow trucks and cement trucks. Among other benefits, the technology provides a better understanding of vehicle activity through power take-off, where mechanical power is transferred to another piece of equipment (such as the cement mixer on a cement truck, for example).
It is this sheer versatility of telematics that has guaranteed it an instrumental (and expanding) role in fleet management for the long term. It is already delivering major improvements to safety, productivity and ultimately profitability, and it is only likely to become more central in the years ahead. Those businesses across the world that integrate telematics systems into their operations can expect to continue to reap significant rewards.
Why is a Telematics System More Thank Just a Vehicle Tracker?
While vehicle tracking is one important attribute of telematics systems, telematics performs a range of other functions as well. Besides its vehicle tracker capabilities, there are three main areas where telematics systems can deliver real improvements. These are enhancing and simplifying communication, raising standards of driver behaviour, and facilitating better workflow through technology and software integration.
Ongoing communication between vehicle units and fleet operator headquarters is essential to fleet management. Operators need to keep in touch with drivers not just to keep track of their location, but also to assign jobs, provide in-vehicle feedback, and so on. But drivers, at the same time, need to be free to do their work – being contacted by phone or text, for example, is a distraction they could do without. Telematics technology helps to rationalize much of this communication, so that operators can provide automated messages, keeping drivers up to date without distracting them from their jobs. This helps to enhance both productivity and road safety.
Telematics systems provide fleet managers with exceptionally detailed insights into the way their drivers behave when behind the wheel. In particular, telematics systems can highlight particular instances and patterns of bad behaviour while driving. Dangerous driving conduct such as tailgating, excessive speeding, rough cornering and harsh braking can all be flagged up to managers by telematics systems. In this way, telematics can support ongoing training programs and serves as an invaluable tool to support continuous improvement.
Because telematics data provides finely detailed insights into driver behaviour, it also enables fleet managers to devise training and development programs tailored to address the particular shortcomings of individual drivers. So, for example, if a driver demonstrates a persistent tendency to brake harshly, their managers can alter their ongoing development program to include training in this specific area. Fleet operators can also use driver telematics data to encourage a degree of healthy competition among the workforce. One way of doing this would be to set up a league table, with the safest drivers rewarded for their efforts. Additional rewards could be offered to those drivers who have made the biggest improvements with regard to safety. Schemes such as this should help to create good-natured competition while simultaneously providing an attractive incentive for better behaviour on the roads. This is all part of the wider task of creating a culture of good road safety.
Telematics also helps to enhance road safety through technology integration. Teletrac Navman’s DRIVE app comes equipped with a comprehensive range of in-vehicle tools to connect the field with the office, including instant two-way messaging, job dispatch (with navigation, driver ID, driver feedback, proof of delivery and workflow management. In addition, telematics is a living system, allowing fleet managers to manage operations by exception, creating standard work processes and highlighting activity which breaks this mold.
Freight exchange platforms allow fleet operators (and owner-operator sole traders) to trade spare vehicle capacity, which helps them to maximize productivity and reduce excess capacity. These platforms connect users and enable fleet managers to put any spare capacity they might have to more efficient use. Telematics systems can help to facilitate this kind of freight exchange by providing instant alerts when a new load has become available and sharing status updates with exchange partners, as well as using GPS data to match vehicles with available loads in their general vicinity. Telematics also helps to simplify the management of workflows and increase job dispatch accuracy. Teletrac Navman also offers a range of other integrations through its Connect+ app hub, including with Fleet Check (allowing users to access fuel card data, for example).
Telematics systems greatly simplify scheduling and routing by integrating them with vehicle tracking and driver performance. As well as allowing for more efficient scheduling, telematics systems provide fleet managers with real-time information on vehicles’ progress, and allow for reactive re-routing where necessary – for example, where disruption is anticipated on the roads, telematics systems can provide an alternative route and instantly notify the driver. This also means better standards of customer service, as it helps to make sure that deliveries reach clients sooner than they otherwise would. In addition, telematics also allows for enhanced maintenance scheduling. Odometer-based service alerts enable managers to ensure that vehicle maintenance tasks are completed according to schedule.


